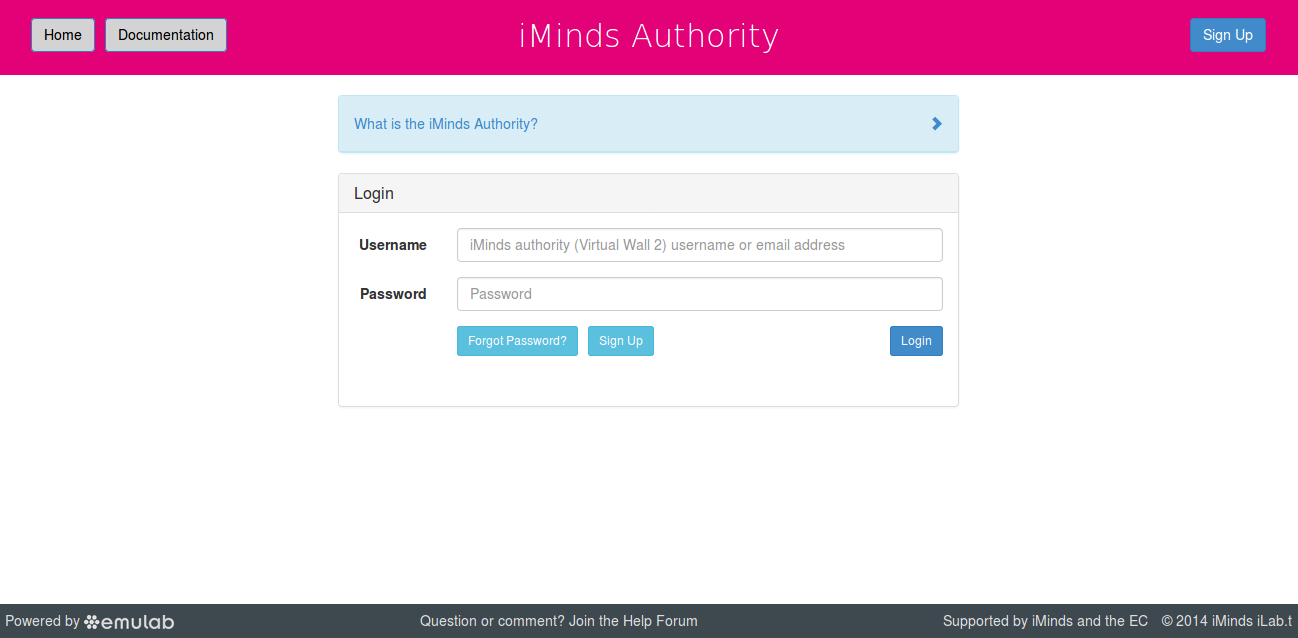
The first step is to access the website (https://authority.ilabt.iminds.be) and Click on Sign Up to request a new account.
 website: https://authority.ilabt.iminds.be
website: https://authority.ilabt.iminds.be
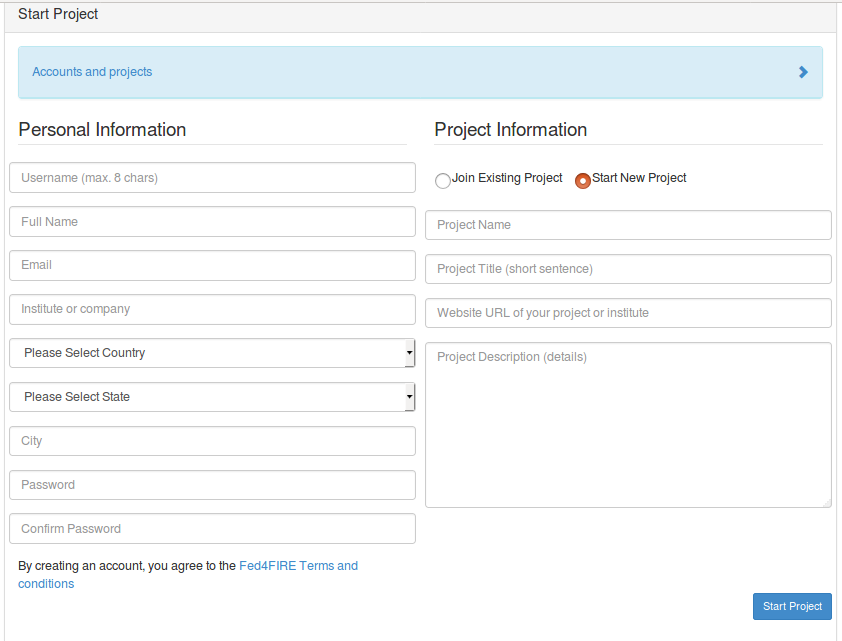
Now, here we will start with creating a new project by clicking Start New Project. If you have been invited to a Project, just click Join Existing Project (or you might have received a specific URL). Fill in the fields and click Start Project.
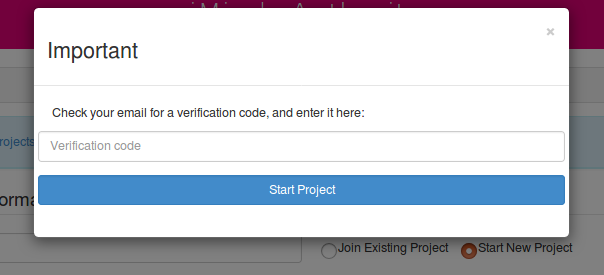
If all goes well, you will receive an email in your mailbox with a code to verify your account which you have to fill in the diablog box.
Now, it can take some time to have a Fed4FIRE administrator or project administrator approved your request. You will receive an email when that is done. After that, you can login on the authority portal.
Note: This tutorial was done on the Linux operating system. We recommend using it.
You need to install PuTTY.
You do not need to install java: it is bundled with the installer.
You need to install java 8 manually.
You do not need to install java: it is bundled with the installer.
But make sure that you start the jFed installer by downloading it, and then right-clicking and choosing ‘Open’.
To install the jFed experiment GUI, go to the jFed downloads page, and follow the instruction there.
Using jFed
If you have an account from https://authority.ilabt.iminds.be, you can download the certificate, and store it locally on your pc. Save the file with extension .pem
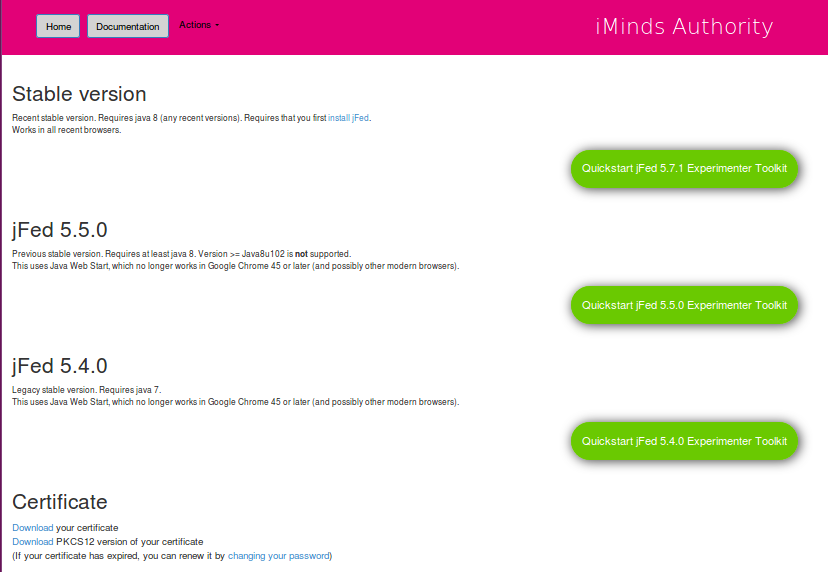
There are 2 basic methods to log into jFed:
1 - Login with Fed4FIRE-credentials or
2 - Login with PEM-certificate

1 - Enter your data.
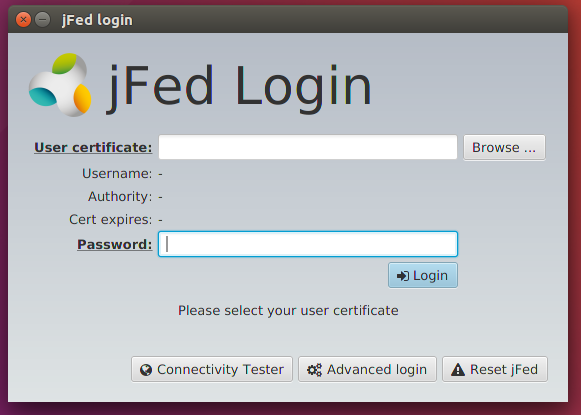
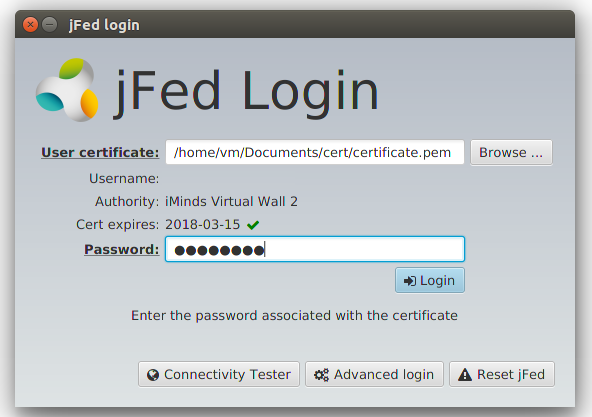
2 - Open the certificate file you downloaded, provide your password and press the login button.
After you login for the first time, a dialog box will pop up to say that you have to configure jFed for this initial run. You typically do not need to make any changes, but it might be good to check out the settings.
When you have logged in you will see the jFed interface with no experiments loaded
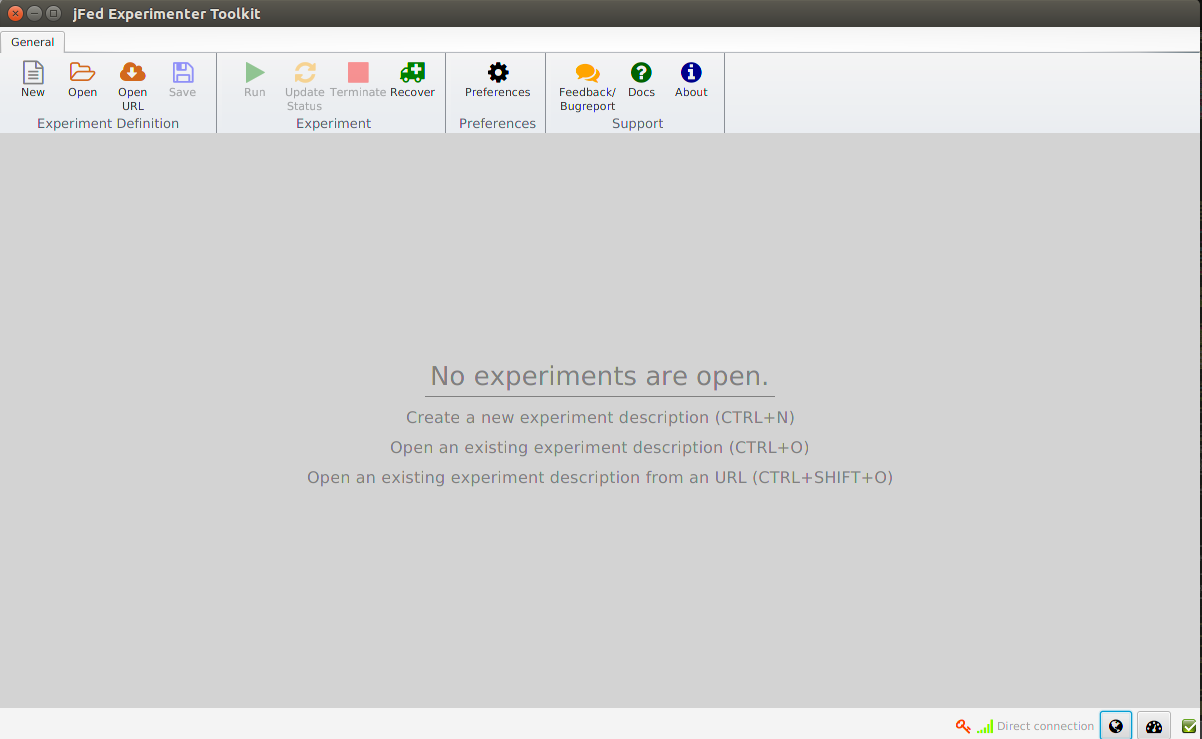
When you click New, you get a blank canvas in which you can draw your experiment.
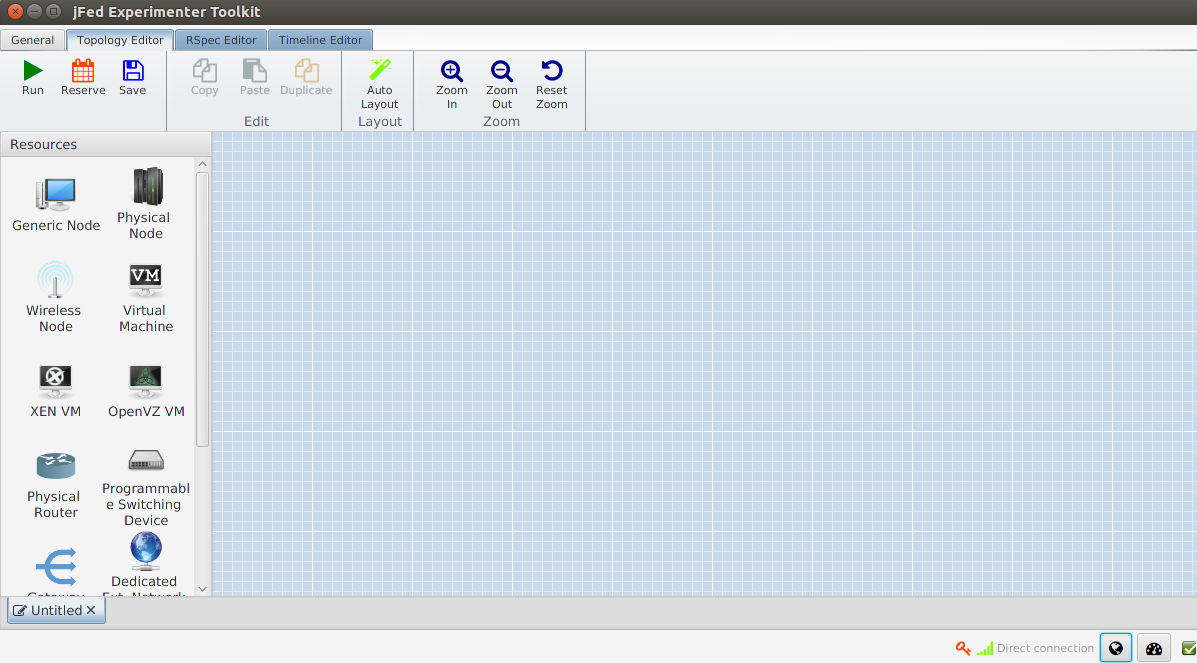
Let’s drag in a wireless node from the left side to the canvas.
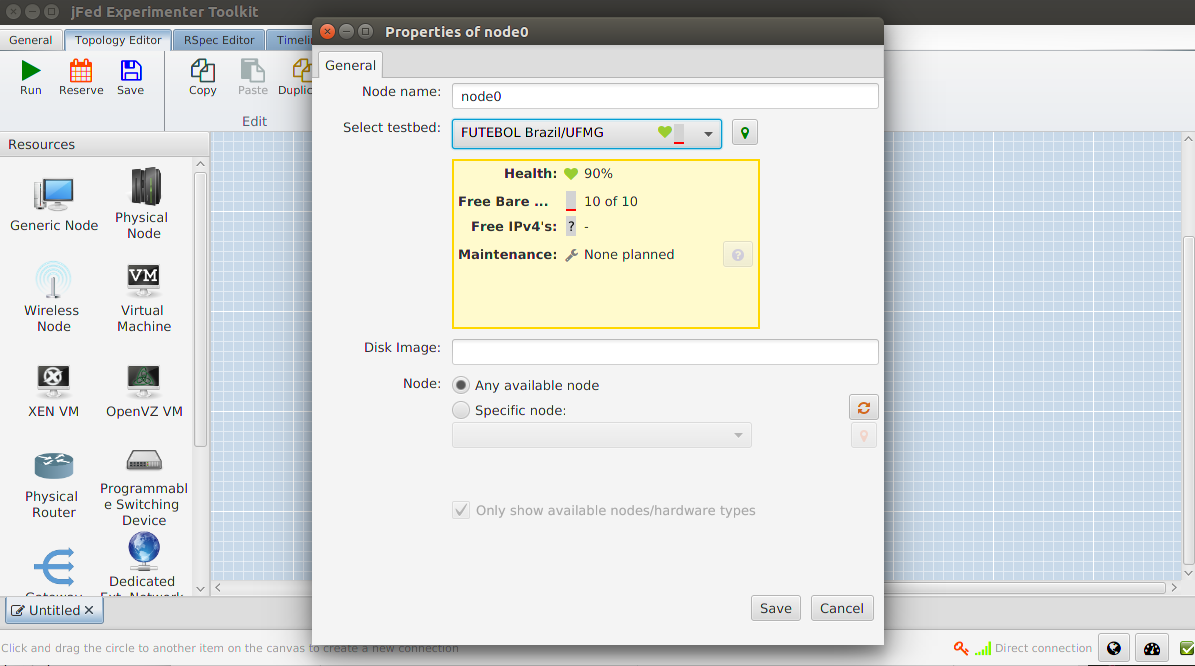
Right-click on the node and change the Select testbed field to FUTEBOL Brasil/UFMG. Click save.
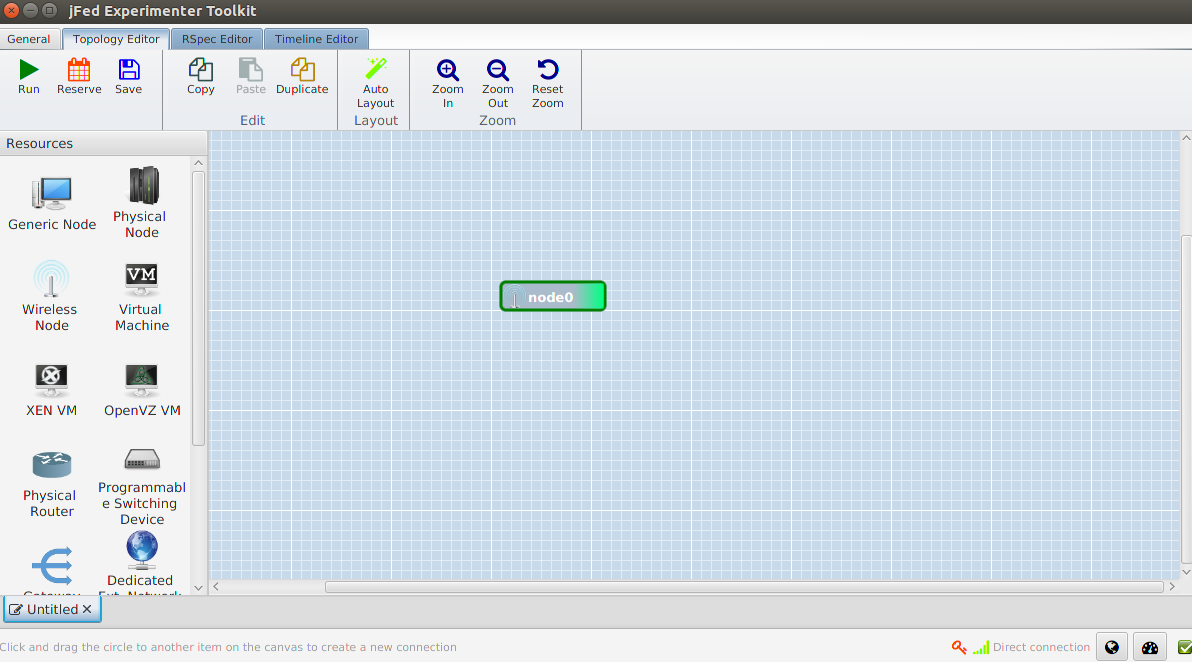
Now click Run and fill in a name and the duration of the experiment.
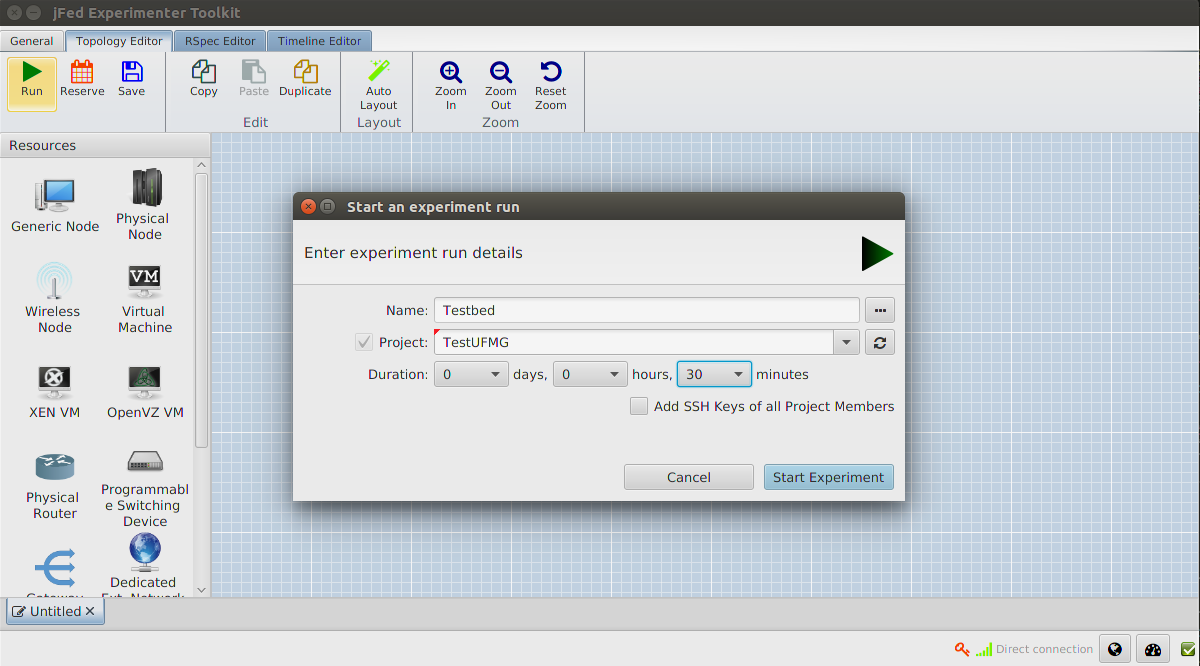
When the node becomes green, we can double click on the node. An SSH Connection will open.
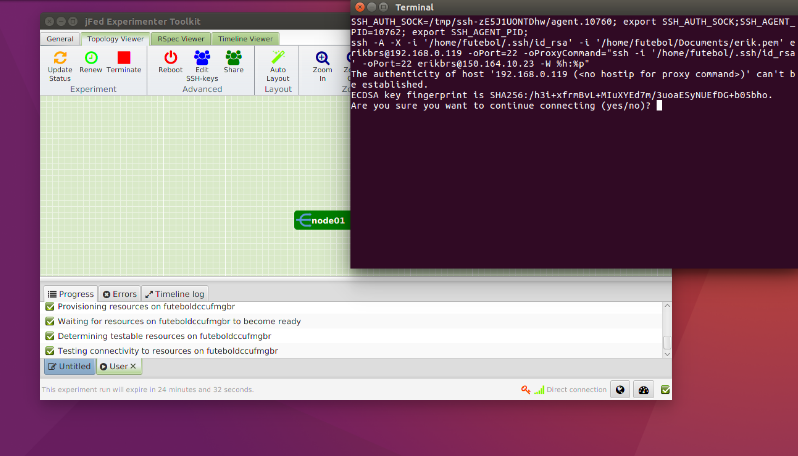
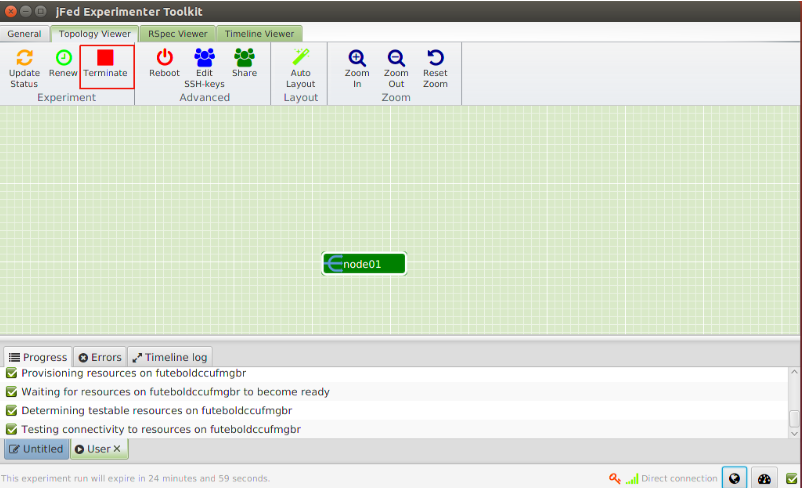
To release your resources before the allocated time or your experiment, you can click on the Terminate button. After that the nodes will become black and if your SSH Connection is still open, you can see that the node will be shutdown.
By using Rspec Editor you can create an experiment and add more advanced features.
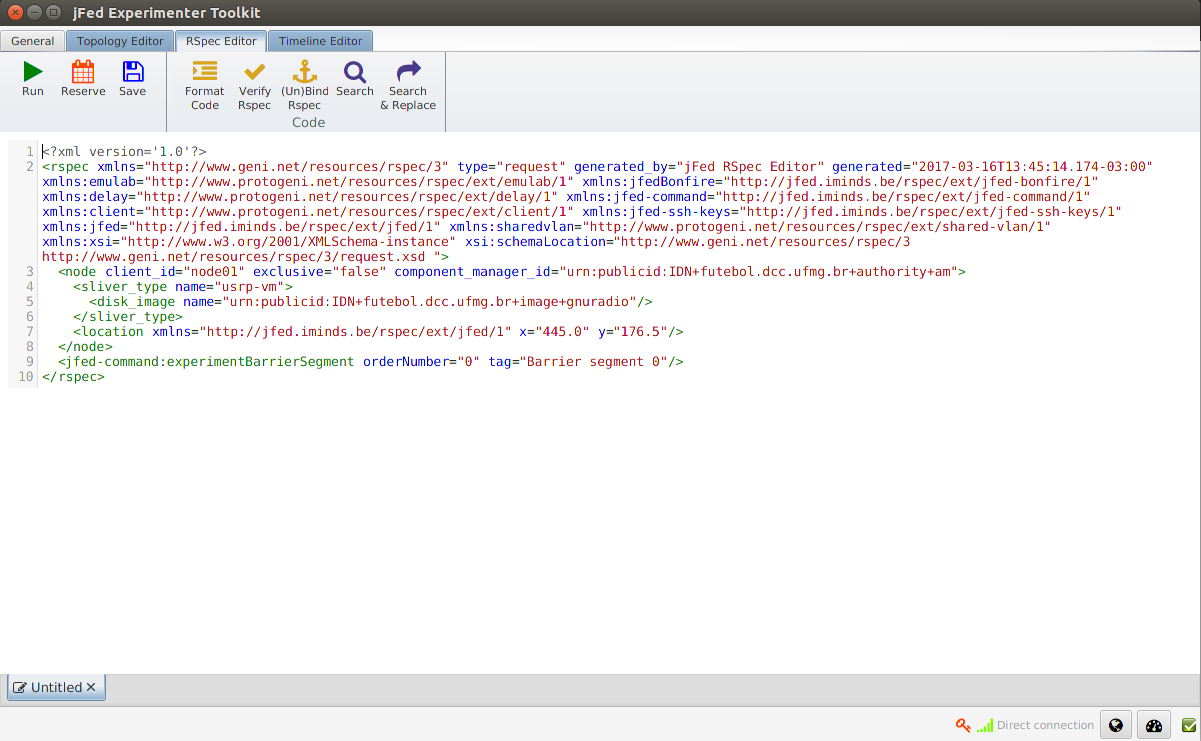
See the fields that you can change. Download our sample file.
node : Specify the client_id and component_manger_id. In the case of UFMG the standard is:
client_id - Any nick.component_manager - urn:publicid:IDN+futebol.dcc.ufmg.br+authority+am
sliver_type name=" " : Choose between available slivers:
usrp-vm
iot-vm
raw-raspberry
There is no image for this sliver at the moment
disk_image name=" " : Each sliver has a disk available, which are:
- usrp-vm
- plain
- gnuradio
- lavras
- iot-vm
- telosb
- raw-raspberry
- There is no image
To select an available disk, simply change the last part of the disk_image string:
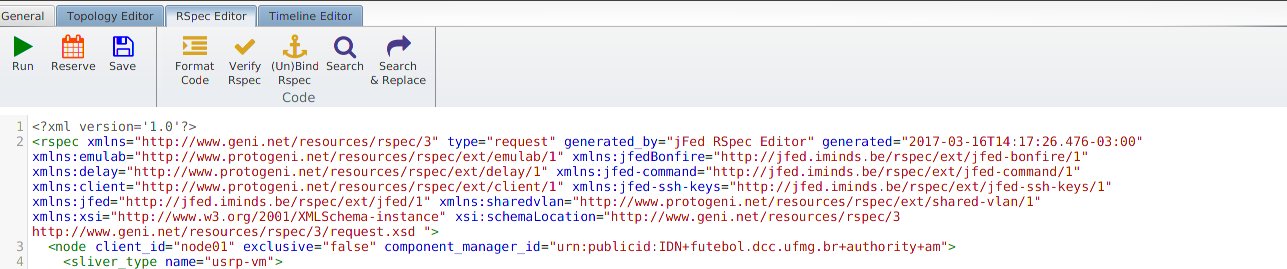
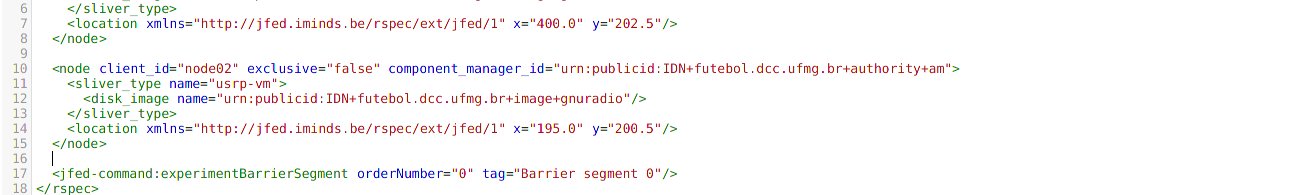
You can create as many nodes as you want by copying and pasting the node tag. Remember to change the client_id for each new node. If you want, you can also change the fields sliver_type and disk_image .
In this example, we have 2 nodes.
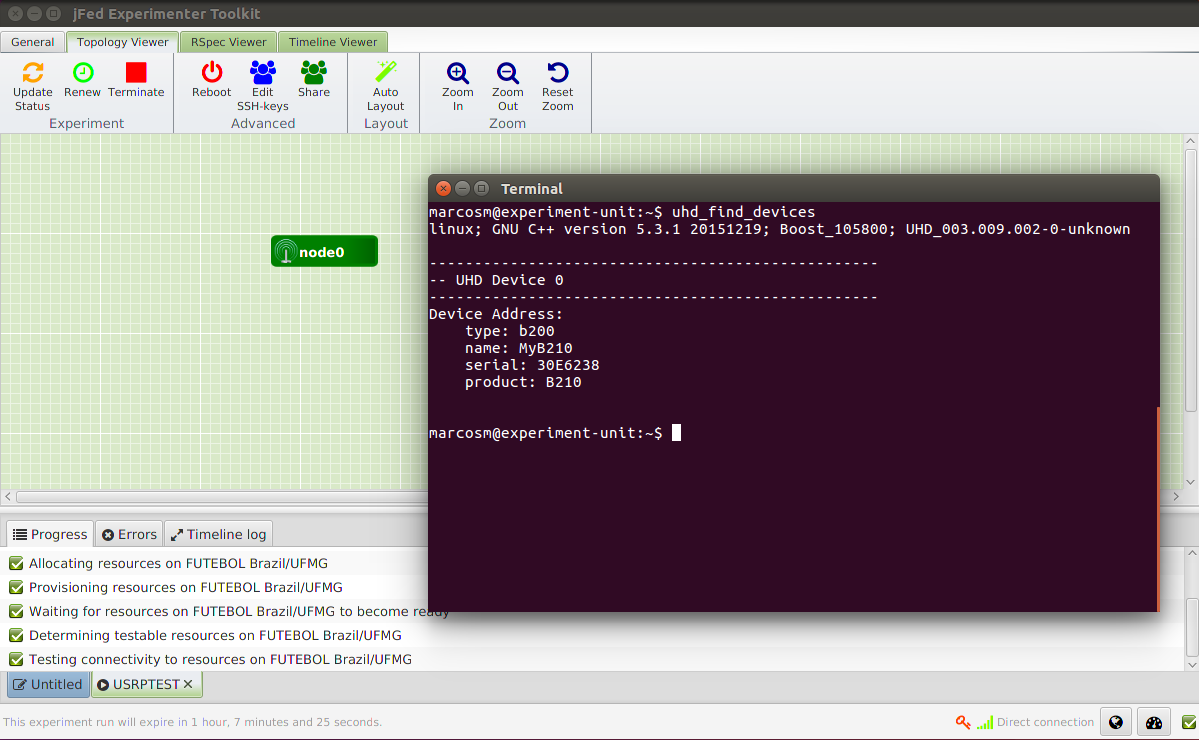
After following step 4.2 you can execute commands to perform experiments in the USRP. The first basic command is to check if the equipment is detected. To do this, run the command uhd_find_devices.
On the ‘rx_node’, run the following code:
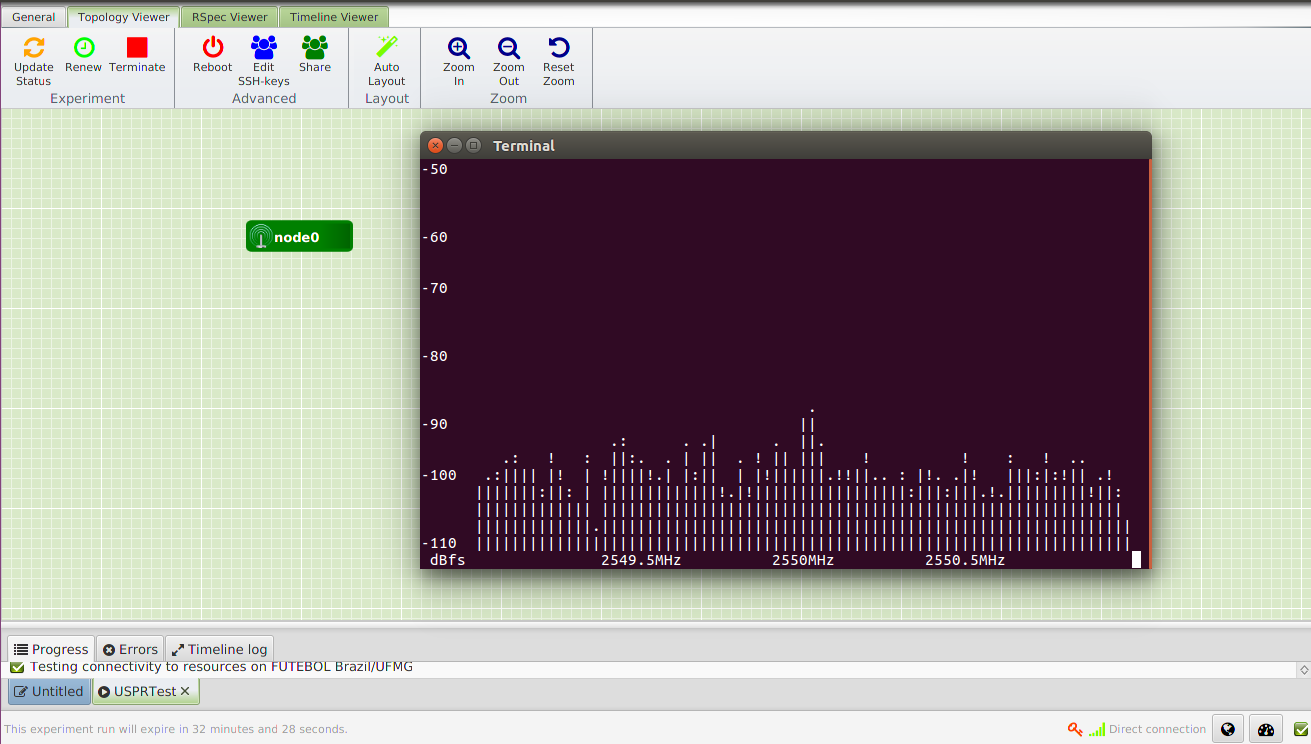
./rx_ascii_art_dft --freq 2550000000 --rate 2000000 --ref-lvl -50
You should be able to see the ascii reprsentation of the transmitted waveform spectrum, as illustrated below:
Project: FUTEBOL
More details: futebol.dcc.ufmg.br
Contact: web-futebol@dcc.ufmg.b
